Surgical Treatment
Gingivectomy / Gingivoplasty
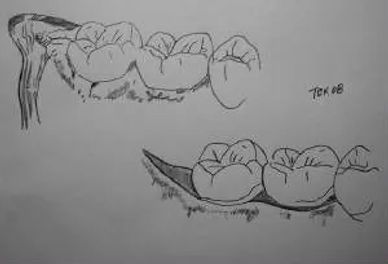
A gingivectomy is a periodontal surgical procedure which includes the removal of a portion of the gingiva (gum tissue ); performed to reduce the soft tissue wall of a periodontal pocket.
Gingivoplasty is a surgical reshaping of the gingiva (gum tissue).
Frenectomy
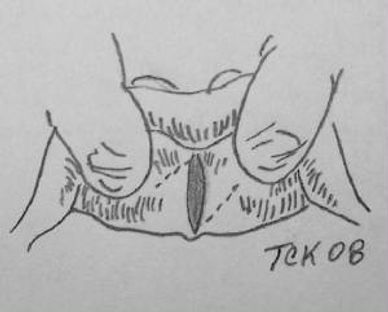
A frenectomy (aka. frenulectomy or frenotomy) is the removal of a frenulum, a small fold of tissue.
The labial frenulum often attaches to the center of the upper lip and between the upper two front teeth. It can also attach to the lower lip and between the lower two front teeth. This can cause a large gap and gum recession. A labial frenectomy removes the labial frenulum.
A series of illustrations of a labial frenectomy procedure (upper lip reflected back in front of nose)
Mucogingival Surgery

This periodontal surgery procedure corrects defects in the morphology, position and/or the amount of gingiva (gum tissue).
A series of illustrations showing one type of mucogingival surgery using connective tissue (upper left lateral and canine)
Osseous Surgery
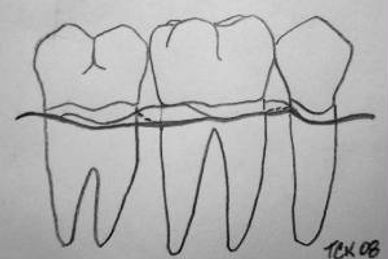
Osseous surgery is a periodontal surgery involving modification of the bony support of the teeth. It creates a bony architecture which is compatible with the maintenance of a physiologic gingival (gum) architecture.
In this series of illustrations bone irregularities caused by periodontal disease (top and lower left) are corrected (lower right)
Crown Lengthening
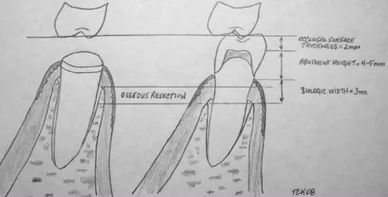
Crown lengthening is a periodontal surgical procedure performed to expose a greater height of tooth structure in order to properly restore a tooth.
Guided Tissue Regeneration
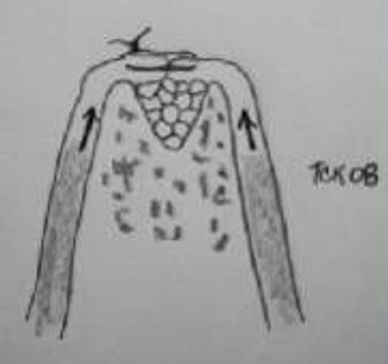
Guided tissue regeneration (GTR) attempts to regenerate lost periodontal structure using a barrier under the gum tissue and over the remaining bone. GTR and the osseous grafting procedure may be performed at the same time.
In this illustration a bone defect is covered by a membrane
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting uses bone to replace a damaged or missing anatomical part of the alveolus (bone supporting the teeth aka. socket). It can eliminate pockets and regenerate the functional attachment apparatus, stabilizing a periodontally compromised tooth or group of teeth.
When a tooth needs to be extracted and you want a dental implant placed in that spot, one of the options is to extract the tooth, place a bone graft, and wait 4 to 6 months for the graft to heal before placing the implant. This is called "socket preservation".
Dental Implants
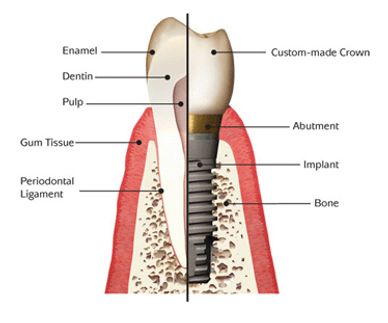
A dental implant is an artificial tooth root that a periodontist places into your jaw to hold a replacement tooth or bridge. Dental implants are natural looking. They are more tooth-saving than traditional bridgework, since neighboring teeth are not altered or necessary for support. Endosteal (in the bone) implants are the most commonly used type (see illustrations below). Dental implants are a viable option in the treatment of partial and full edentulism. The ideal candidate for a dental implant is in good general and oral health. They are considered an excellent option for tooth replacement.